Understanding the Seven Business Cybersecurity Layers
In an era where digital fortification is as crucial as financial investment for businesses, understanding the depth and breadth of business cybersecurity layers is non-negotiable. The seven layers of cybersecurity form a defensive matrix that, when understood and applied correctly, can shield your business from the most cunning of cyber threats.
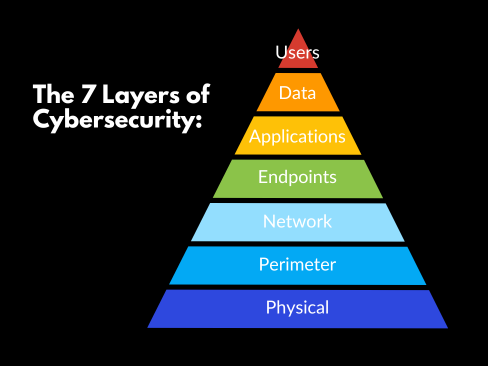 The 7 Layers of Cybersecurity For Business
The 7 Layers of Cybersecurity For Business
As an IT professional, or a business leader striving to safeguard your enterprise’s digital assets, grasping the complexity and necessity of each layer is key to a resilient security posture. From the tangible bulwarks of physical servers to the intangible protocols of user education, each layer serves as a critical checkpoint against cyber incursions. The seven layers of cybersecurity are:
1. Physical Layer
This foundational layer represents the tangible heart of your network: the servers, switches, and various physical access points. It forms the foundation of cybersecurity for critical infrastructure. Neglect here can open the door to direct breaches, so securing these assets is as critical as any digital safeguard.
2. Perimeter Layer
Traditional defenses likened to firewalls are no longer sufficient in a world where remote work has dissolved the conventional office borders. Today, the concept of a perimeter must evolve for remote work cybersecurity to protect data that flows beyond physical walls.
3. Network Layer
Think of this as the central veins of your organization through which all digital lifeblood flows. A critical aspect of network security. It encompasses everything from routers to Wi-Fi networks, and securing it means ensuring that every pulse of data is monitored and protected.
4. Endpoints Layer
These are the frontline devices that your employees use every day, from laptops to smartphones, and extending to IoT devices. Adopting a zero-trust security framework is essential here, ensuring that every access point is verified and secured. We recommend employing a zero-trust strategy with a tool like ThreatLocker’s endpoint protection platform.
5. Applications Layer
Every application, from your accounting software to the ubiquitous Office suite, poses potential risks. These tools must be rigorously assessed and monitored to ensure they don’t become Trojan horses within your tech arsenal.
6. Data Layer
Data is the new gold in the digital economy, and this layer is where your most precious resource resides. Whether it’s stored in cloud services or on local databases, safeguarding it from intrusion is a paramount concern.
7. User Layer
Your employees can be your strongest defense or your greatest vulnerability. Cultivating a robust cybersecurity culture and providing ongoing awareness training is critical to ensuring that cybersecurity is a shared responsibility across the company.
The Number 1 Way Companies Get Hacked
With the ever-growing number of cyber-attacks, understanding the predominant threats is key to safeguarding your business. According to a 2022 FBI report, phishing schemes topped the charts with a staggering number of complaints. Fast forward to 2024, and phishing emails remain the most prevalent tool for digital intrusion, accounting for over 90% of hacking incidents.
While the persistence of email-based threats is alarming, the good news is that implementing robust cybersecurity protocols can significantly mitigate these risks. Let’s explore the three most common attack vector vulnerabilities and how a proactive strategy can secure your network.
Most Common Attack Vector Vulnerabilities
- Email Phishing Attacks: A primary attack vector vulnerability. The simplest of emails can be a wolf in sheep’s clothing, carrying threats from ransomware to spyware. The solution lies in comprehensive staff training on identifying suspicious emails and deploying advanced email filtering systems that keep evolving with new threats.
- Compromised Credentials: Cybercriminals often purchase stolen passwords from the dark web to penetrate networks. To combat this, enforce strong password policies and consider investing in a reputable dark web monitoring service to stay one step ahead. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) isn’t just recommended; it’s imperative for all user accounts, especially since under 20% of Microsoft 365 users have enabled it. Striving for 100% MFA adoption creates a formidable barrier against unauthorized access.
- Software and Device Vulnerabilities: Unpatched software is akin to leaving your front door unlocked. Regularly updating systems and applying patches promptly are non-negotiable practices. Employing vulnerability management tools can help automate this process, ensuring that your defenses are always up to date.
While less common, misconfigurations and insider threats also pose significant risks. Misconfigurations can often be preempted through regular audits of your IT infrastructure, ensuring settings align with best security practices. Insider threats, whether malicious or accidental, require a combination of access controls, monitoring, and an informed culture of security within the workplace.
Remember, the key to cybersecurity isn’t just about reacting to threats—it’s about establishing a proactive stance. With a well-informed team and the right tools in place, you can build a resilient defense against the most common, and even the most sophisticated, cyber threats.
Fortifying The 4 Most Vulnerable Business Cybersecurity Layers Against Attacks
In the battleground of cyber warfare, businesses of all sizes face high-risk vulnerabilities across their network, endpoints, applications, and user layers. A proactive approach to threat prevention within these layers is not just recommended; it’s a necessity. Let’s delve into enhancing security across these critical layers that intersect with the most common ways hackers get in.
Top 4 Most Vulnerable Business Cybersecurity Layers:
Network Security Layer
A robust network security strategy involves more than switches and routers—it’s about creating a resilient ecosystem. Proper segmentation by department can prevent the lateral movement of a hacker, isolating attacks to minimize damage. Techniques like Virtual LANs (VLANs) and strategic firewall placement are fundamental, yet the real power lies in continuous network monitoring and advanced threat detection systems that can identify and respond to anomalies in real-time.
Endpoint Protection Layer
Gone are the days when a firewall alone would suffice. In today’s landscape with rampant compromised credentials, every device is a potential entry point. Embrace Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions and ensure all remote and mobile devices adhere to your security protocols. Regular updates and patches are a must, but complement these with behavioral analytics to detect unusual actions that could signify a breach.
Application Security Layer
Applications are the lifeblood of your operations, from standard office software to specialized business tools. MFA/2FA should be non-negotiable for access, while Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) principles ensure that trust is never assumed, always verified. To further shield your applications, adopt Ringfencing™ strategies which create an operational barrier, restricting applications to only essential processes and interactions, thus reducing the attack surface.
User Education Layer
Cybersecurity is as much about people as it is about technology. The most sophisticated security infrastructure can be undone by a single uninformed click. Continuous training and simulations of phishing attacks are crucial in fostering a vigilant workforce. Regular updates on the latest threat scenarios during team meetings will keep cybersecurity as a top-of-mind concern. Encourage skepticism and instill a zero-trust philosophy across all levels of your organization to combat social engineering and other tactics that target human vulnerabilities.
By addressing these layers with the right strategies and technologies, you can significantly bolster your company’s defenses. Remember, a well-prepared organization doesn’t just resist attacks—it makes them increasingly difficult to even attempt.
 Strategically Reducing Your Cybersecurity Exposure
Strategically Reducing Your Cybersecurity Exposure
To effectively shrink your organization’s attack surface, understanding the technical visibility of your assets to threat actors is key. A reduced profile equates to fewer opportunities for breaches. Chief Security Information Officers (CISOs) should be prepared to address these critical questions:
- Remote File Access: How are employees accessing sensitive files while working remotely? The method of access should ensure that data transmission is secure and that files are only accessible via secure channels.
- Cloud Infrastructure: If your organization utilizes cloud services, are they configured with security best practices in mind? Proper configuration and regular audits can prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- VPN and RDP: The use of VPNs should be standardized for remote access, and public-facing RDP servers should be avoided due to their high susceptibility to brute-force attacks. Implement secure remote access tools with multi-factor authentication for enhanced security.
- Internally Hosted Applications: For applications hosted internally and accessed remotely, consider implementing secure web gateways or ADCs. These can provide robust security measures without the need for a traditional VPN, simplifying access while maintaining security.
Balancing security with ease of use doesn’t have to be a zero-sum game. With the adoption of advanced cybersecurity technologies and methodologies, organizations can protect their assets while still offering a seamless user experience. CISOs must navigate these waters carefully to ensure that security measures enhance, rather than hinder, organizational productivity.
Streamlining Defense: Essential Tools To Minimize Your Cyber Risk
In the digital terrain, much like the natural world, predators often target the most visible and vulnerable. In cybersecurity, this means that businesses with a larger attack surface are more likely to face threats. To stay ahead of the pack and off the radar of cyber predators, consider implementing the following types of applications:
- Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP). These applications provide comprehensive security solutions that prevent, detect, and respond to threats at the device level, all without impeding the user experience.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)/Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS). These tools monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and block potentially harmful traffic, effectively reducing your exposure to attacks.
- Secure Web Gateways (SWG). SWGs enforce company policy compliance, filtering unwanted software/malware from user-initiated web/internet traffic and providing insights into outbound data.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB). If you’re utilizing cloud services, CASBs offer a critical control point for securing cloud applications, and mediating between your users and cloud service providers.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM). IAM solutions manage digital identities and their access to various IT resources, ensuring that only the right people have access to the right resources at the right times.
Each of these applications operates with the dual goal of security and simplicity, ensuring that your network remains robust against threats without placing undue burden on your infrastructure or your team.
RELATED: IT Pro’s Playbook: How To Block Cyber Threats In 2024 with action items now available for download. Get your free copy here deep dive into securing the 4 most exploited layers of cybersecurity.
 Network Hardening: Fortifying Your Cyber Defenses
Network Hardening: Fortifying Your Cyber Defenses
Network hardening is an essential practice that transforms default system settings into a fortified security posture. The goal is not just prevention, but active defense against potential attacks.
While Windows systems are built with user-friendliness in mind, their default settings often prioritize ease of use over stringent security. This is where tools like PingCastle become invaluable, especially for those utilizing Windows Active Directory. PingCastle simplifies the auditing process, offering a rapid assessment to tighten security measures and highlight areas that need immediate attention.
Pro Tip: Scrutinize your network’s privileged accounts, narrowing them down to only those essential for necessary operations and compliance requirements. Accounts with perpetual password lifespans present a serious security risk. Implementing the principle of least privilege is not just best practice; it’s a cornerstone of a hardened network.
Before applying any changes, IT leaders must thoroughly vet and understand the potential impact to ensure business continuity. To see network hardening in action and explore PingCastle’s capabilities, we invite you to watch our in-depth webcast featuring a live PingCastle demonstration.
Implementing The Principle Of Least Privilege: A Key To Secure Access
Neglecting the principle of least privilege is a common pitfall that can lead to significant security vulnerabilities. This principle dictates that individuals should be granted the minimum level of access — or permissions — necessary to perform their job functions, and nothing more. This not only tightens security but also minimizes the potential impact of a breach.
Granting granular access rights is an investment in your organization’s security and an important step in cybersecurity best practices. The time and resources spent are negligible compared to the potential costs of a data breach. Hackers often exploit overly permissive access settings, which can lead to extensive damage if they gain entry to your systems.
Actionable Steps:
- Conduct an audit of current access levels across your organization to identify any instances of excessive permissions.
- Establish clear roles within your organization and assign access rights based on these roles.
- Regularly review and adjust permissions to ensure they align with current job requirements, especially after role changes or departures.
By rigorously applying the principle of least privilege, you can significantly strengthen your organization’s defense against malicious actors and ensure that, in the event of a compromise, the scope of what they can access is strictly limited.
Best Practices For Access Control Among High-Level Users
When setting up user access, the highest privileges often carry the highest risks. It’s not uncommon for CEOs and top IT personnel to have unrestricted access through a single account used for all purposes, a practice borne from convenience but fraught with risk.
The best practice is to delineate access by providing two distinct accounts for VIP users: one with administrative privileges for technical tasks and another, a “daily driver,” for routine operations like communication and basic work functions. This cybersecurity tip for business ensures that if the everyday account is compromised, the administrative privileges remain secure and separate, greatly reducing the potential damage an attacker can inflict.
Implementation Tips:
- Use the admin account exclusively for tasks that require elevated permissions, such as configuring systems or managing user accounts.
- Conduct daily business activities through the regular account, which should have standard user permissions to minimize risks.
Adopting this dual-account approach not only reinforces your security posture but also instills a culture of conscious access management throughout the organization.
 How Often Should You Scan Your Network For Vulnerabilities?
How Often Should You Scan Your Network For Vulnerabilities?
For businesses of all sizes, the integrity of network security is not a set-and-forget affair; it necessitates ongoing vigilance. The deployment of robust security measures is a step in the right direction, yet the true test of their efficacy lies in regular and rigorous testing.
While there is no one-size-fits-all answer to how often you should conduct these checks, a good rule of thumb for enterprises is to perform comprehensive security assessments quarterly, with more frequent, lighter checks or scans monthly. Factors such as compliance requirements, the sensitivity of data handled, or recent security incidents can necessitate more frequent evaluations to prevent cyber attacks.
The choice typically lies between engaging with a seasoned cybersecurity consultancy or MSSP to rigorously assess your security posture, or waiting for a breach to reveal the cracks in your defenses — the latter often resulting in significant financial and reputational damage.
Proactive engagement with cybersecurity experts to conduct penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and security audits is not just a safeguard but a business imperative. They can provide an objective analysis of your defenses, identify the unseen weaknesses, and guide you through the remediation process — a strategic investment that pales in comparison to the costs and consequences of a security breach.
Kickstart Your Business Cybersecurity Layers Defense with 7tech’s Cybersecurity Assessment
Business cybersecurity layers may not directly contribute to profits, but it’s the shield that guards the lifeblood of your modern business: technology. Without secure technology, the risk of operational paralysis is high, turning cybersecurity into an indirect profit protector.
In today’s digital-first business landscape, delaying cybersecurity enhancements is akin to leaving your doors unlocked in a bustling marketplace. Don’t wait for a breach to be the wake-up call. Proactively fortify your defenses by conducting a comprehensive cybersecurity risk assessment with 7tech. Identify your vulnerabilities, understand your risk areas, and formulate a robust defense strategy.
Connect with the seasoned experts at 7tech to navigate your cybersecurity landscape. Call us at (844) 701-MSSP or book a discovery call to initiate your tailored risk assessment journey today.
Neal Juern, CEO of 7tech, is a seasoned cybersecurity advisor known for his strategic insights in Zero-Trust Cybersecurity. It’s his passion to help businesses protect their data. If you’re interested in doing that in-house, then check out his free Masterclass.







